- MSIT to provide the direction for implementing STI policies which address national and social issues
The Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Lim Hyesook; MSIT) worked with other relevant ministries in setting the direction for establishing the “5th Science and Technology Basic Plan (2023~2027),” which specifies the mid-to-long-term direction for science, technology and innovation policies. On August 18, the basic plan was finalized at the steering meeting of the deliberation committee of the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology.
The Science and Technology Basic Plan is established by the Minister of Science and ICT and is the highest-level plan in S&T field, which outlines the national S&T policy direction for the next five years. Each central government and local government establish and carry out annual implementation plans for tasks under the basic plan.
※ Legal ground: Article 7 of the framework act on S&T (S&T basic plan)
The direction which was finalized this time introduced the results for analyzing external and internal S&T environment, the direction for implementing STI policies, the system for establishing the 5th S&T basic plan and the process.
In the past, MSIT finalized the direction for establishing the basic plan through internal reporting. In order to strengthen the collaboration between the S&T Advisory Council and relevant ministries from the planning and establishing stages of the 5th S&T basic plan, the direction for establishing the basic plan was proposed and adopted as the agendas for the deliberation meeting of the S&T Advisory Council.
The agendas are as follows.
① Analysis of external and internal environment
Due to the rapid digital transformation after the COVID-19 outbreak, there have been changes in overall economy and society, and there are emerging global issues such as technological hegemony and climate change.
[ Analysis of current situation and future prediction ]
Category |
Current situation analysis |
Future prediction |
Technology |
Intensified competition between the U.S. and China over technological hegemony |
Trade blocs created centering on allies, regulations on technology expanded |
Economy |
Regional blocs formed in global market, industries and jobs undergoing great transformation |
The gap between countries widened, polarization increased |
Society |
Demographic cliff, contactless lifestyle has become the norm |
Regions no longer strong, an increase in social conflict |
Environment and security |
Efforts to achieve carbon neutrality, living with risks |
Global efforts to preserve the environment and respond to risks |
In order to respond to national agendas, major countries such as the U.S., China, EU and Japan proposed the direction for implementing STI policies, which are based on not only technology development but also policy measures in society. The implementation system was also overhauled.
[ Recent policy trends in major countries ]
|
ㅇ (U.S.) Increase investment on strategic technologies and climate change, legislate Endless Frontier Act
ㅇ (China) Establish 8 strategic industries and 7 strategic technologies, national efforts made for securing strategic technologies
ㅇ (EU) Inject 95.5 billion euros in R&D investment for research and innovation, develop self-reliance in 6 strategic technology areas
ㅇ (Japan) Establish legal basis and implementation system for innovative policies, which solve national priorities with science and technology
|
② Direction for implementing innovation policy
In the 5th Science and Technology Basic Plan, the scope of policies will be expanded to further advance the existing science and technology policy. Based on the concept of NIS 2.0 in the ways to innovate national R&D (Jul. 2018, plenary session of the Presidential Advisory Council on S&T), the measures to innovate the entire country and society will be established.
[ Comparison between innovation policy and the existing S&T policy (example) ]
Category |
Existing S&T policy |
STI policy |
Policy direction |
Focus on promoting science and technology |
Trade blocs created centering on allies, expand regulations for technologies |
Enhance R&D capacity of regions for promoting science and technology |
Encourage regions to be self-sustaining using S&T to address the issues of weak regions |
Goals |
Quantitative input and output |
Qualitative effects of policies |
Double the investment volume for basic research |
Increase GDP by 1 billion won per 100 million won R&D investment made |
Policy scope |
Policy tool focused on R&D |
Encompass R&D and non-R&D |
Educate scientists and engineers, support researchers |
Educate scientists and engineers, support researchers
+ visas for foreigners, innovation in operating universities, tax exemption for new recruitment etc. |
The Ministry of Science and ICT will work with other ministries to propose national goals and directions for implementing STI policies as well as the divided roles among different ministries. In the process for establishing policies, the collaboration among S&T experts, relevant ministries and research institutes in the field of economy, humanities, and society such as KDI, STEPI, and KIET will be strengthened.
[ Comparison between the existing plan and the 5th S&T basic plan (example) ]
Respond to the Fourth Industrial Revolution |
|
Respond to digital transformation |
ㅇ List up R&D policies and programs of ICT ministries, summarize the contents
ㅇ Experts in ICT and S&T to mainly participate in establishing the policy
ㅇ Check progress in carrying out ICT R&D projects by each ministry and achievements in formulating policies |
|
ㅇ Set the goal and direction for implementing digital transformation policies through partnership with ministries in charge of economy and society
ㅇ Experts from interdisciplinary fields such as employment, education, and industry to participate in the establishment process
ㅇ Track the progress in targets achieved in implementing digital transformation policies as well as the roadmap of each ministry in meeting targets |
In addition, in the process of formulating the basic plan, the main contents of the existing science and technology policy and progress made in implementing the policy, such as S&T future strategy 2045, which is a mid-to-long term S&T policy direction, and the existing S&T basic plan (1st~4th plan) will be analyzed and developed further.
③ Structure of the basic plan (tentative)
The 5th S&T basic plan enhances STI capabilities and establishes strategies and tasks for resolving issues faced by society. The plan also outlines key performance indices, which reflect challenges of policy goals and outstanding characteristics of achievements.
[ Structure of the 5th S&T basic plan (example) ]
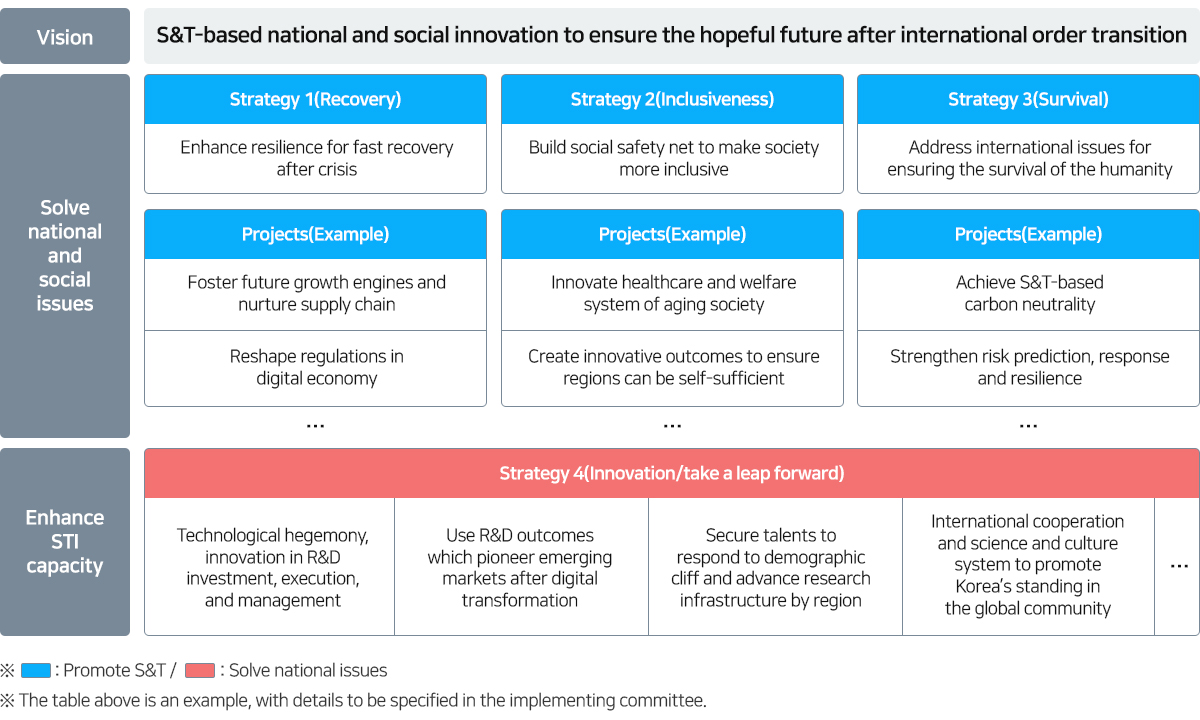
From technological perspective, national strategic technologies (about 20) identified by government will be proposed, based on policy trends of major countries such as the U.S., China, and EU. Korea’s response direction will be suggested by analyzing domestic and overseas trends of each technology area, current status of R&D, and vulnerabilities.
※ Dramatically reduce technology cases compared to the current figure (100 or so), present response measures by analyzing domestic and overseas trends, current status of R&D, and vulnerabilities → provide ways to make investment in each field in the mid-to-long-term national R&D investment strategy
④ System and procedure for establishing the basic plan
In order to establish the basic plan, the Ministry of Science and ICT will form and operate a committee to implement the S&T basic plan, where experts in S&T, economy, humanities, and society participate. In the process for establishing the basic plan, multiple stakeholders including the committee under the Presidential Advisory Council on S&T, relevant ministries and institutions, stakeholders in each field, and citizens take part and play roles such as proposing agendas and planning projects.
|
❶ (Presidential Advisory Council on S&T) Members from the private sector who belong to the Presidential Advisory Council on S&T and the deliberation council participate as founding members.
❷ (Relevant ministry) Propose policy agendas from the early stage of establishment, align it with policy direction of ministry
❸ (Participating institutions) Support the establishment of the basic plan and identify various policy agendas and policy measures
❹ (Stakeholders) Collect and reflect feedback from relevant stakeholders in each field such as association by work area and occupation
❺ (Citizens) Take part in various methods such as contest, hackathon, and gathering feedback from internet
|
The Ministry of Science and ICT plans to form the committee to implement the S&T basic plan in September 2021. Under the leadership of the committee, the draft of the 5th S&T basic plan will be formulated by March 2022. After that, feedback from multiple stakeholders will be collected to complement the contents and the plan will be finalized by 2022.
Vice Minister Lee Gyung-Su of Science, Technology and Innovation said, "at a time when international order transition is expected in areas such as economy, society, and diplomacy due to COVID-19 and the competition between the U.S. and China to gain technological hegemony, the future of Korea should be reshaped based on science, technology, and innovation, following industrialization, democratization and entry into advanced nations."
"To this end, science and technology policies are required to ensure the survival and security of nations. The Ministry of Science and ICT plans to enhance the role of science and technology to address issues faced by society."
"Together with relevant ministries and industry, academia, and research institutes from S&T, economy, and society sectors, the Ministry of Science and ICT will carry out S&T-based innovation policies to achieve four goals, which are national innovation, economic recovery, social inclusion, and survival of humanity."
For further information, please contact Deputy Director Han Chol-hwan (E-mail: hancholhwan@korea.kr) of the Ministry of Science and ICT.